The Electromagnetic Calorimeter
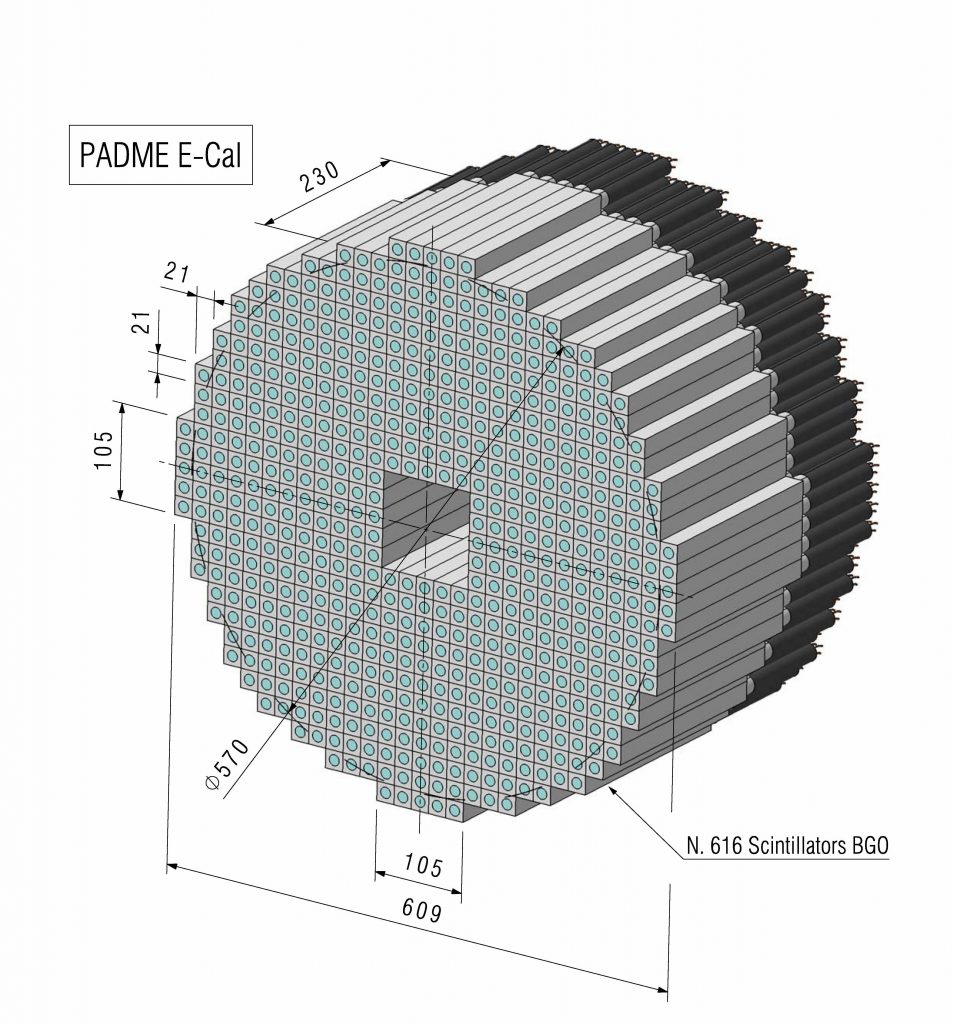
Layout of the crystals of the PADME e.m. calorimeter.
The PADME calorimeter (ECAL) is a homogeneous crystal calorimeter with an approximately cylindrical shape, with a diameter of ~600 mm, depth of 230 mm, and with a central square hole 105×105 mm2.
The active volume is composed by 616 BGO scintillating units (210x210x230 mm3), obtained by machining the crystals recovered from one of the end-caps of the electromagnetic calorimeter of the dismantled L3 experiment at LEP CERN. The readout of the calorimeter is performed by means of photomultipliers [HZC XP1911] glued on the backward face of each crystals.
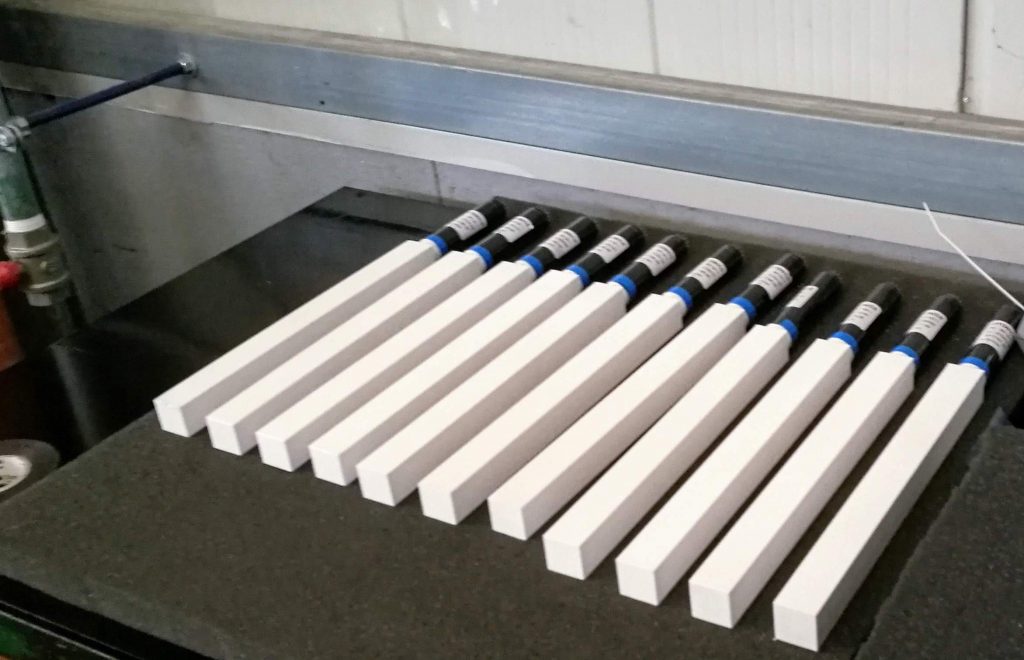

Scintillating units of the main PADME e.m. calorimeter. They consist of a BGO crystal and a photomultiplier.
The calorimeter central hole serves to avoid the interaction of the high rate Bremsstrahlung photons emitted in the positron beam direction.
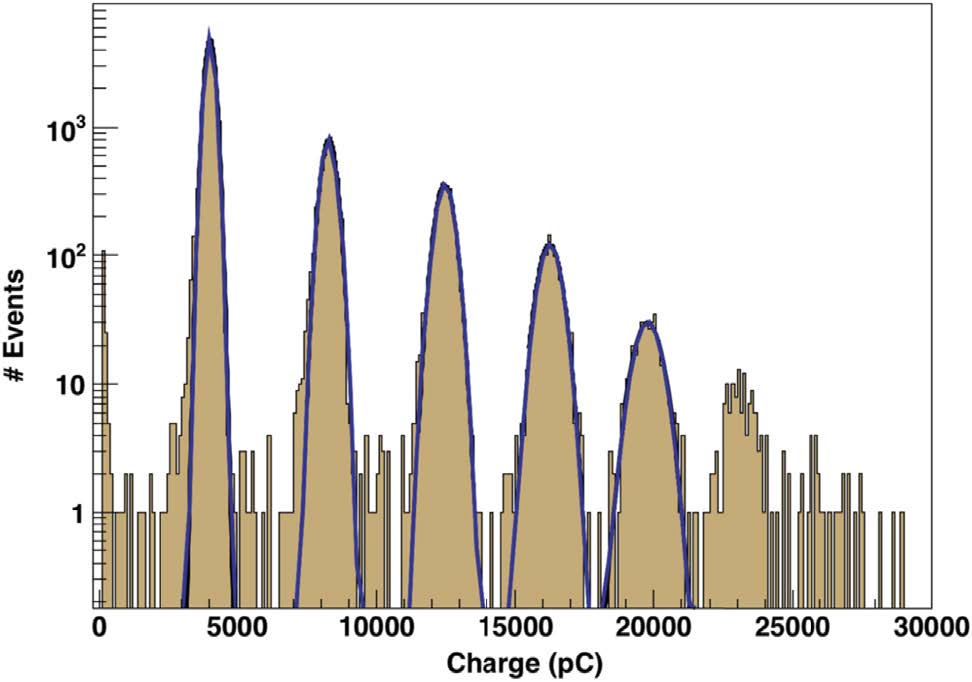
The scintillating units performance has been characterized in a dedicated test beam with a 250 MeV electron beam. The total reconstructed charge can be seen in the right picture. The individual peaks correspond to one, two, etc. electrons impinging the scintillating units. A fit on the collected charge with the sum of five Gaussians is also shown. A second data collection has been performed increasing the beam energy to 450 MeV.
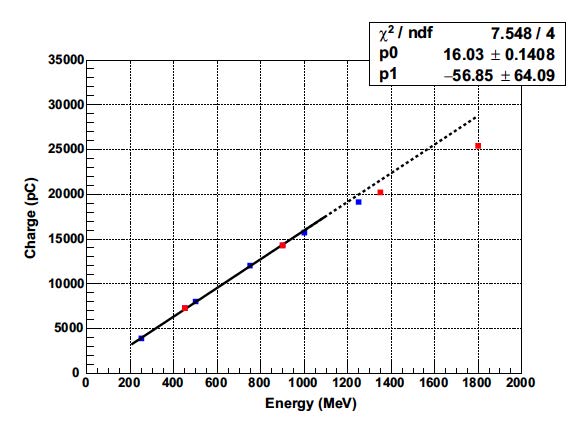
The position of the maximum of each Gaussians allows to extract of the relation between the collected charge and the deposited energy.
The figure below shows the relation between the reconstructed charge and the beam energy.